Jews: The Flood (2106 - 2105 BC) - lasted 5 months - according to the Biblical chronology. … All the sources of the great abyss were opened, and the windows of heaven were opened … (Genesis 7, 11)
Old Testament:
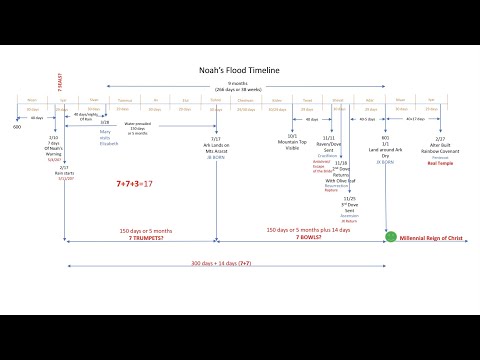
11 In the six hundredth year of the life of Noah, in the second month, on the seventeenth day of the month, on this day all the springs of the great deep were opened, and the windows of heaven were opened;
12 And it rained on the earth forty days and forty nights.
19 And the waters on the earth became exceedingly strong, so that all the high mountains that are under all the heavens were covered;
20 the water rose fifteen cubits above them, and the mountains were covered.
21 And every flesh that moves on the earth, and birds, and cattle, and beasts, and every creeping thing that crawls on the earth, and all people, lost its life;
22 Everything on dry land that had the breath of the spirit of life in its nostrils died.
23 Every creature that was on the surface of the earth was destroyed; from man to cattle, and creeping things, and birds of the air - everything was destroyed from the earth, only Noah remained and what was with him in the ark.
24 The water grew stronger on the earth for one hundred and fifty days.
Greeks: there were 3 floods - Ogygov, Deucalion, Dardan, according to Servius - 2, according to Istrus 4, according to Plato - many
Holocene of Northern Europe. The climate at this time was generally warmer than the current one. It was preceded by the Boreal period, when the climate was similar to the modern one, and was followed by the Subboreal period, transitioning to the present. As the hottest period of the Holocene, the Atlantic period is often referred to as the Holocene climatic optimum. In North Africa, the Neolithic subpluvial roughly corresponded to the Atlantic period.
8000 - 6000 BC - World Flood (based on reconstruction of the absolute age of the flood from a data array from around the world)
6200 BC e. - the most severe global cooling of the Holocene, abnormal for the warm Atlantic period. It lasted from 200 to 400 years, during which the climate changed significantly
5500 BC e - rise of the water level of the Black Sea by 140 m Theory of the Black Sea Flood
7000-3000 BC The Neolithic subpluvial is the latest of the "Wet Sahara" or "Green Sahara" periods, during which the region was more humid and had a richer and more diverse biota, including human population, than in the modern desert. A. Wilkinson dates the end of the subpluvial around 3300 BC. e.
Promotional video:
3900 BC - the drought, which prevailed before the onset of the subpluvial, returned, mass desertification began, and the Sahara Desert reappeared. Dry conditions persist to this day.
2106 - 2105 BC Global Flood (according to the Bible)
approx. 1000 BC - the common ancestor of the Eastern Slavs and Indians (R1a) lived 3000 years ago
mid 1st millennium BC e. - The Sub-Atlantic period began with the end of the Iron Age cooling and the beginning of the Roman climatic optimum, which lasted until the beginning of the 4th century AD. e. It was at this time that classical antiquity belongs
599 - 528 BC lived Mahavira
563 - 483 BC e lived Buddha
approx. 500 BC e - the West European Atlantic haplotype is located from the East Slavic one in five mutation steps - 520 generations to a common ancestor, 2500 years of difference.
V-IV centuries. BC BC Classical Greece
336 - 30 - the era of Hellenism (supposedly)
323 - Ptolemy, Pharaoh of Egypt
235 - 200 - Greco-Bactrian kingdom, Euthydemus.
180 - 10 - Indo-Greek kingdom
27 - 476 (Constantinople - up to 1453) Roman Empire
54 - invasion of Britain
33 - annexation of Mauritania to Rome
30 - Egypt became a Roman rule, execution of the last king of Egypt
27 - submission by August tribes north-west of Spain
17 annexation of northern Spain to Rome
15 - Tiberius's campaign against the Alpine mountaineers
13 - a treatise on the architecture of Vitruvius - summarized the experience of Greek and Roman construction
8 - Tiborius reached the Elbe and captured 40 thousand Germans.
6 BC BC - Judea comes under the control of Rome
2 BC e - the birth of Jesus.
=====
11 - Catastrophic flood, accompanied by a complete change of the Yellow River
19 - More than 4000 Jews were expelled from Italy
79 - Vesuvius eruption
354 - the beginning of the Great Migration (IV-VII c)
410 - Capture and sack of Rome by the Visigoths
449 - Capture British Angles, Saxons, Utes and Frisians.
476 - The overthrow of the last Western Roman emperor Romulus Augustulus by the German Odoacer. The traditional date of the fall of the Western Roman Empire.
536, 540 and 547 - three violent volcanic eruptions that triggered the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to 660, dust clouds covered the sky in the Northern Hemisphere and the sun did not show for a whole year, which led to cold, hunger and plague epidemics
536-538 - Famine that killed 80% of the population of North China.
6th century - the beginning of the chronology system from the birth of Christ (the calculations were made by the Roman monk Dionysius the Small)
approx 600 - the Europeans have an anonymous manuscript Mappae clavicula, in the 12th century - its second version, translated from Greek. into Latin, containing recipes for making handicraft materials, including metals, glass, mosaics, dyes, technical data on how to build the foundations of bridges and buildings, a work undoubtedly based on ancient traditions.
793-880 - 13 years were associated with famine and floods, and 9 years with extremely cold winters and epidemics. At this time, leprosy spreads in Central Europe.
859 - the first mention of Novgorod
862 - Rus, Slovenia, Chyud, Lop, Krivichi came to the Varyag, and asked the rulers for themselves, and got out of their family Rurik
921 - Book of Ibn Fadlan
965 - The Book of Al-Masoudi
985 - the book of Al-Mukaddasi
X-XIII- Medieval Warm Period - an era of relatively warm climate in the northern hemisphere, which followed the climatic pessimum of the Great Migration Period and preceded the so-called Little Ice Age of the XIV-XVIII centuries. It was characterized by mild winters and relatively warm and even weather. The interval of the medieval climatic optimum is the foundation of Scandinavian settlements in Greenland, as well as the growth of cities in North-Eastern Russia.
1096-1272 - crusades to Palestine
1147 - the first mention of Moscow
From the 11th century. - Karelians begin to bury without cremation, from the 12th century. graves with coffins.
1168 - Fall of Arkona, Baltic Slavs
1198-1411 - Northern (Baltic) Crusades
1200 - 4 major volcanic eruptions
1203 - “A natural disaster brought about significant changes. The Holy Land (?) Was shaken by a chain of earthquakes of greater magnitude than those that occurred in 1154 and especially in 1170, which left all the fortresses in very poor condition. For this reason, the Templars did not receive funding for the Fourth Crusade.
1223 - Battle on the Kalka river
"Word about the death of the Russian land"
1232 -1240 - crusades to Novgorod
1260 - presumably trepidation (precession). Within 30 years after that, trepidation ended. Alphonse the Wise of Castile took the trepidation at first for the existing one, but later abandoned this assumption. It is possible that just in his time, the precession period again "calmed down" after another violation. French astronomers testify to this in 1300 and at first made calculations with a compromise correction (Campanus de Novare (1261-64)), but already from about 1290 on the example of the Toledo tables they preferred constant annual cycles and used from 1328, based on practical reasons. Observation of the phenomenon of trepidation is a direct indication of the instability of the earth's axis after a shock and a gradual regaining of stability.
1263 - The first signs of a prolonged crisis appeared that affected Europe during the early Middle Ages.
mid-13th century Rubruk
13-15 centuries - active construction in Europe of dark red brick artel production
1300 - 1850 - Small Ice Age (with intervals of warming), 8-13 centuries. - small climatic optimum
beginning of XIV century - End of medieval warming. This period saw numerous documented cases of mass starvation and epidemics, in particular, plague. During this time, many villages were abandoned and deserted. It is estimated that the population of Central Europe has dropped by almost half.
1346-1353 - plague pandemic in Europe
1455-1485 - War of the Scarlet and White Rose
14-16th centuries - Unification of the Russian lands around Moscow. Formation of a single Russian state.
16th century - Orthodox Muscovites come to the faculty of the middle Volga region.
1492 - the beginning of construction of dark red bricks in Russia, restoration by Ivan lll of the white-stone Kremlin with the participation of Italians
1547 - translation of Vitruvius into French, published in Paris
1550 -1860-small ice age. At this time, major social upheavals occur (Thirty Years' War, the Great French Revolution). In parallel, after the late Renaissance, the Age of Enlightenment and industrialization began.
1584 - Stone Order - to promote stone construction, and lend bricks and white stone to the townspeople in installments for 10 years. the first stone buildings were churches. Residential buildings of stone were erected by the population with great reluctance. And it's not just the high cost of stone housing. In ancient times, there was a strong belief that living in such buildings is extremely harmful to health. Monks who humble the flesh and prison prisoners whiled away their days in stone chambers. And during the construction of residential buildings, the dampness of "cold" stone was preferred to "live" wood. In addition to churches and monasteries, only commercial premises were erected from stone. However, by the end of the 17th century, stone buildings were considered prestigious. At the same time, all the wooden churches of the capital were replaced by stone ones.
1589 - the independent Moscow Patriarchate is formed.
1601 - 04 - unusual cold weather in Russia led to crop failure and famine, the beginning of the Time of Troubles
1703 - foundation of St. Petersburg
1783 - the eruption of Laki, Iceland
1805 - I. Elagin (the book "Experience of the Narrative about Russia")
1815 - eruption of Mount Tambor, Indonesia, triggered a "year without summer"
1850 - third cold interval
2020 - the year marked as the beginning of an increase in the risk of asteroid activity
2100 - by this year the level of the oceans will rise by 65 centimeters