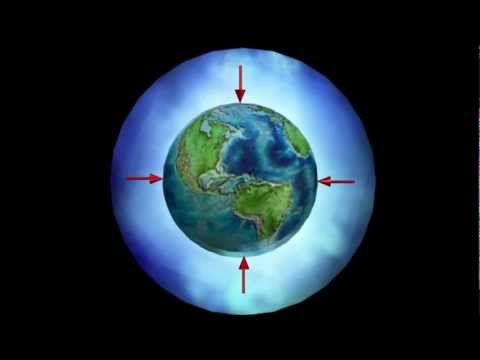
They just wrote on the network that an absolute minimum of atmospheric pressure was recorded in Moscow. I ask my usual question - why? Not explained, just stated. I look in directories. They write about moving eddies, anticyclones, cyclones, etc. But this movement is secondary. It occurs just when there are pressure drops in adjacent zones. But why these drops occur - silence. We think further ourselves. Even "scientists" agree that pressure is what is described everywhere as the pressure of the "overlying column of air" on an area equal to a conventional unit. The higher we rise along this pillar, the shorter it will become for us and the less pressure will be put on us. It is obvious. This means that if in Moscow it is raining and snowing stupidly, there are no eddies and even wind, while, they say, the pressure is small, it comes out,the air column over Moscow has become shorter. This is also understandable. What determines the length of the post? They say to us "atmosphere", I understand - the Dome. I take a map of the world with pressure indicators, mentally build it on a circular plane with a cent at the North Pole and Antarctica along a circular perimeter, and I see that the closer to the middle, the more pressure, and the closer to the edges, the less. I hope it's clear why? The dome cover is not flat, but spherical. The longest "air column" supports it in the center, and the shortest ones - at the edges. The map confirms this. This means, I draw the final conclusion, if the pressure force depends on our position under the Dome, and it changes, it turns out that the Dome is not at all solid, but plastic and flexible, the surface of which is subject, let's say, to wave-like vibrations, as a result of which it can sag,why the "air column" in this place is noticeably shortened.
In my opinion, the hypothesis is interesting, especially since I have never heard it in this form anywhere before …;-)